Embryonic Stem Cells Adult Stem Cells

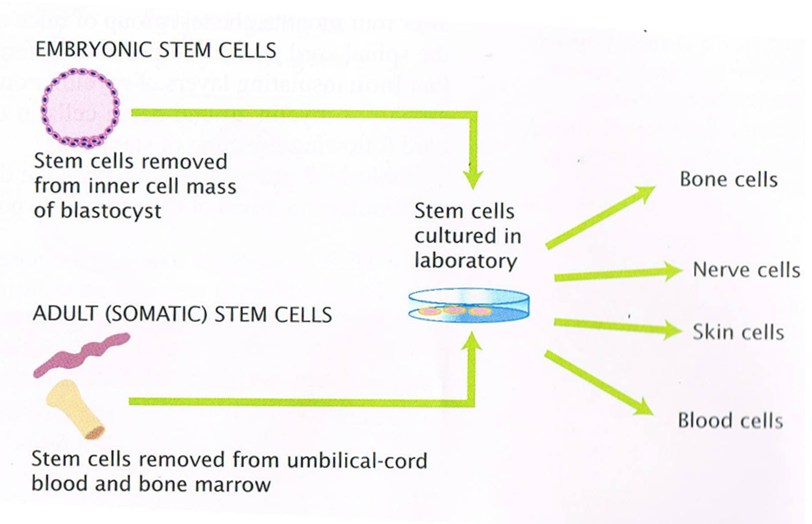
Embryonic Stem Cells, on the other hand, are stem cells that are derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst. Blastocyst is an early-stage of the embryo that it …
· Wound Healing: 114 for embryonic stem cells vs. 330 for adult mesenchymal stem cells, 565 for adult epithelial stem cells For a more detailed analysis, take a look at the American Stem Cell Therapy Assocition (ASCTA) white paper on adult stem cells vs. embronic stem cell research .
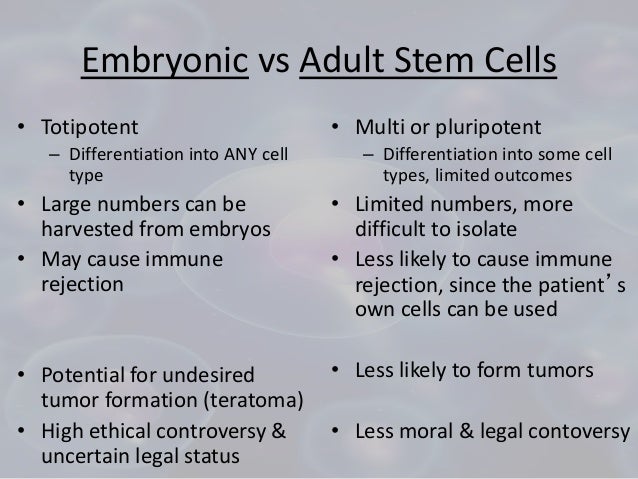
Stem cells, directed to differentiate into specific cell types, could offer the possibility of a renewable source of replacement cells and tissues to treat many diseases. Cons One of the main objections to embryonic stem cell research has to do with the belief that using embryos tampers with life.
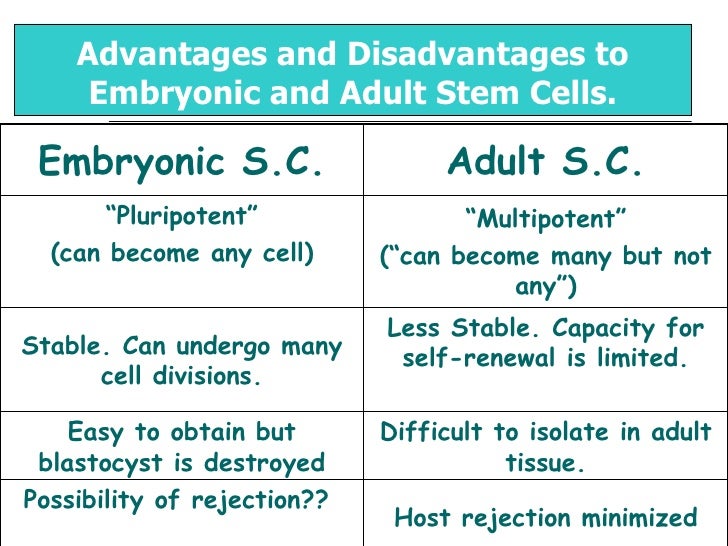
Embryonic Stem Cells, on the other hand, are stem cells that are derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst. Blastocyst is an early-stage of the embryo that it …
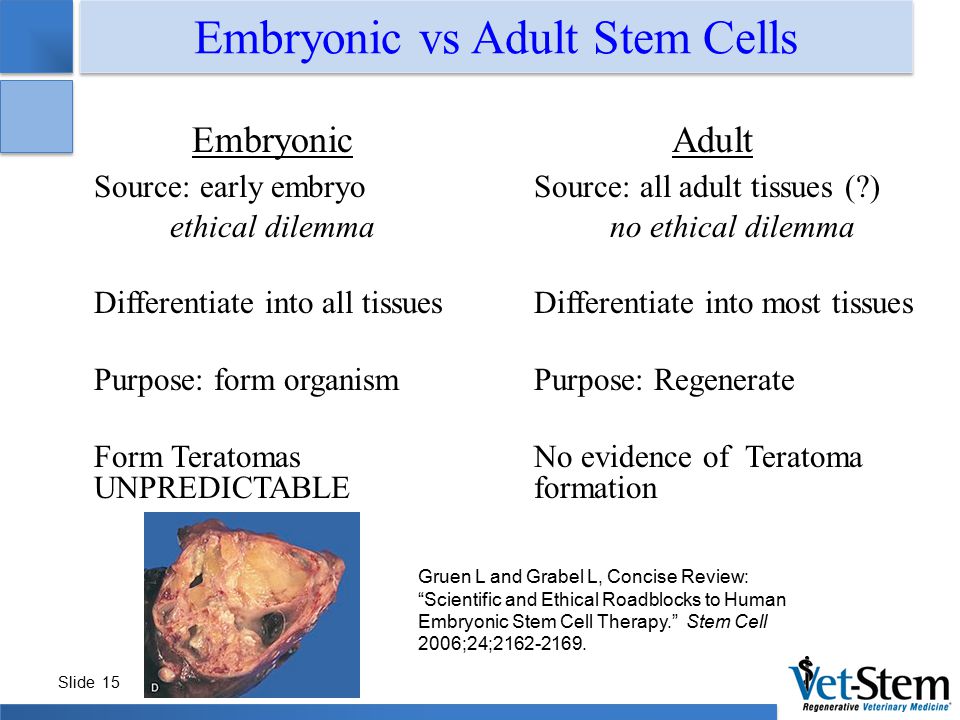
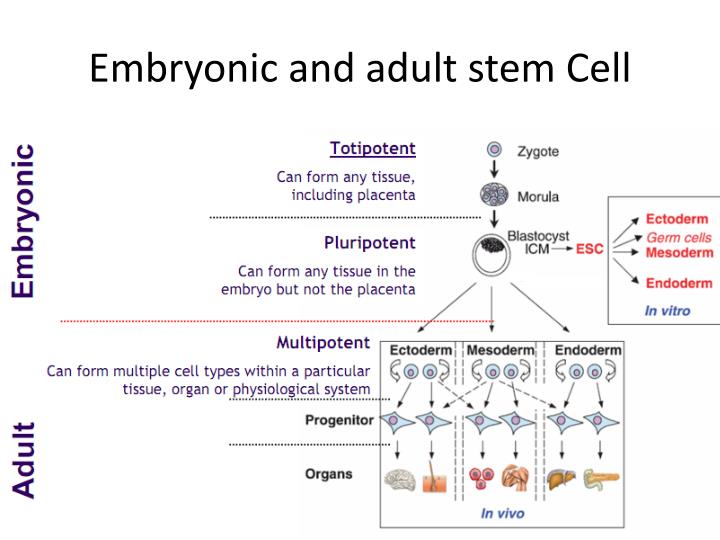
Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent, meaning they are able to grow (i.e. differentiate) into all derivatives of the three primary germ layers: ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm.
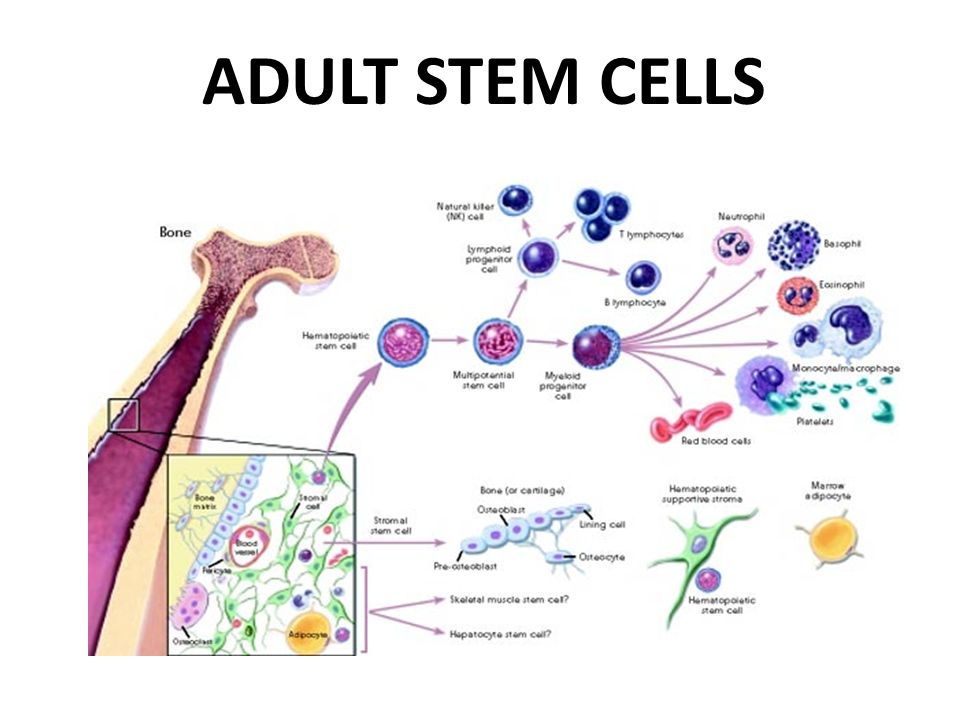
Adult stem cells (ASC’s) are found in everyone’s body and they are capable of repairing a host of tissues. In fact, the research on adult cell lines has surpassed embryonic. Above is the result of a search I did yesterday in the National Library of Medicine, looking at all embryonic stem cell published papers vs. the total on all adult stem cell lines.
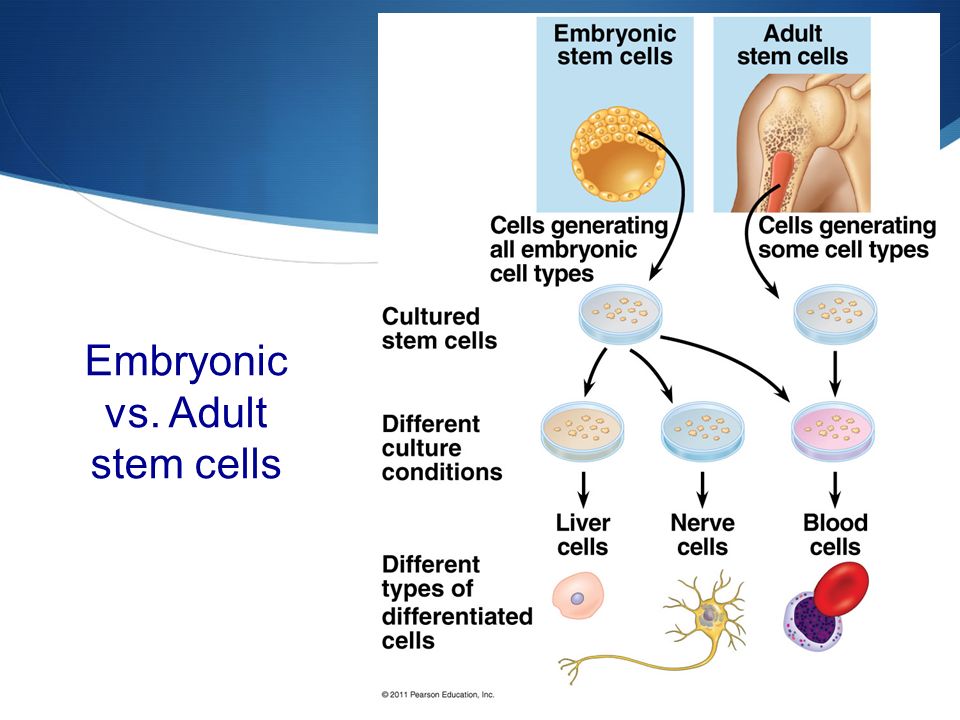
Jan 11, 2010 · The human embryonic stem cells are first isolated by removing the inner cell mass into a plastic laboratory culture dish that contains a nutrient medium or broth called the culture medium.
Unlike embryonic stem cells, the use of adult stem cells in research and therapy is not controversial because the production of adult stem cells does not require the destruction of an embryo.
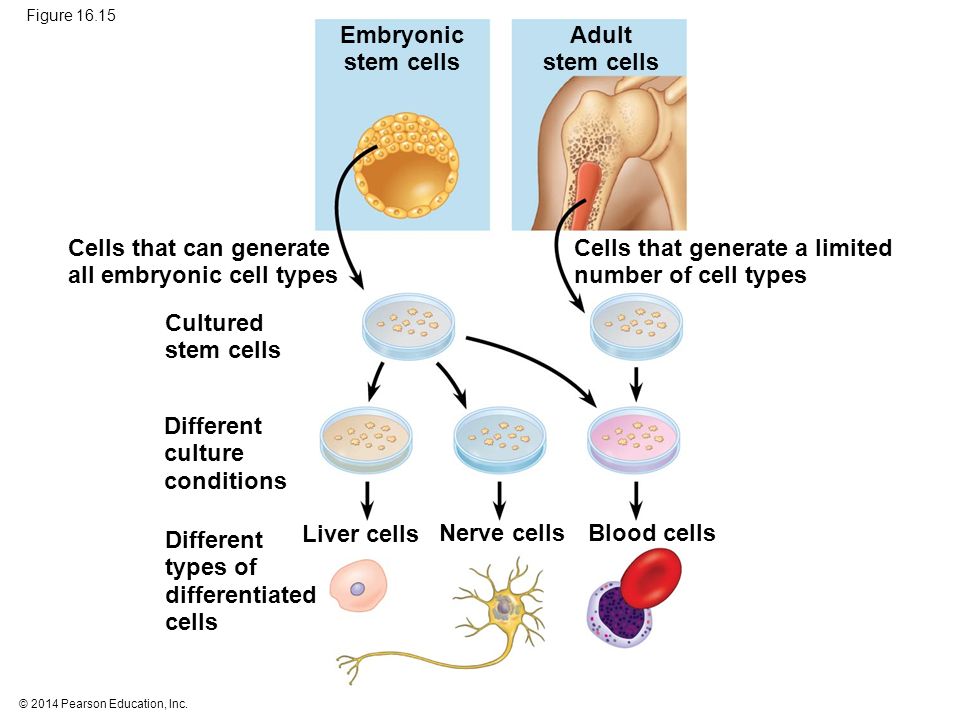
Adult stem cells are rare in mature tissues, so isolating these cells from an adult tissue is challenging, and methods to expand their numbers in cell culture have not yet been worked out. This is an important distinction, as large numbers of cells are needed for stem cell replacement therapies.
Embryonic stem cells possess the capacity to divide for long periods and retain their ability to make all cell types within the organism. These are termed pluripotent stem cells.